A research team led by Lih Y. Lin and Fred Rieke from the University of Washington (UW) has developed a novel and highly targeted method by harnessing quantum dots for activating neurons in the brain in order to understand the way of communication of nerve cells. This technique may pave the way to treat brain disorders such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's disease and even psychiatric disorders.
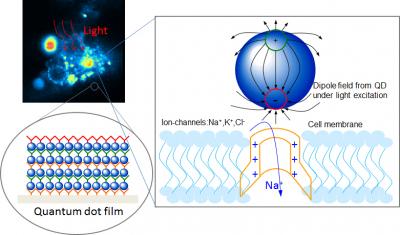 Optically excited quantum dots in close proximity to a cell control the opening of ion channels. (credit:Lugo et al., University of Washington)
Optically excited quantum dots in close proximity to a cell control the opening of ion channels. (credit:Lugo et al., University of Washington)
The study has been reported in Biomedical Optics Express, an open-access journal of the Optical Society. In the study, the research team cultured cells over quantum dot films in order to allow the cell membranes to be in close contact with the quantum-dot coated surfaces. It then measured the single cells’ electrical behavior by exposing them to flashes of light of different wavelengths. The light agitated electrons inside the quantum dots produce electrical fields that activated spiking in the cells.
According to Lin, after successfully culturing prostate cancer cells on the quantum dot films, the research team carried out the test on cortical neurons in order to analyze the characteristics of neurons. What the team found was the possibility of exciting neurons and other cells as well as controlling their activities remotely utilizing light. This non-invasive technique is flexible enough to study and control cells at various locations, while reducing unwanted effects.
Rieke informed that this technique allows activation of nerve cells in a temporally and spatially controllable mode. It is helpful in knowing neural circuits’ typical activity patterns by introducing perturbations and observing their impact in restoring normal circuit activity.
The research team has until now used the technique in cells that are cultured outside the body. It intends to use the technique inside live tissues in order to understand processes of diseases and be clinically effective. To achieve this, Lin explained that the quantum dot surfaces need to be modified in order to target particular cells when delivered into live animals. The quantum dots used have to be non-toxic to avoid harmful effects on the cells. One solution is to use silicon for synthesizing non-toxic quantum dots.