May 15 2020
Several people would have undergone a CT scan at a certain point in their life—sliding in and out of a tunnel, with a huge machine rotating around. X-ray computed tomography, well-known by its acronym CT, is a technique extensively used to capture cross-sectional images of objects.
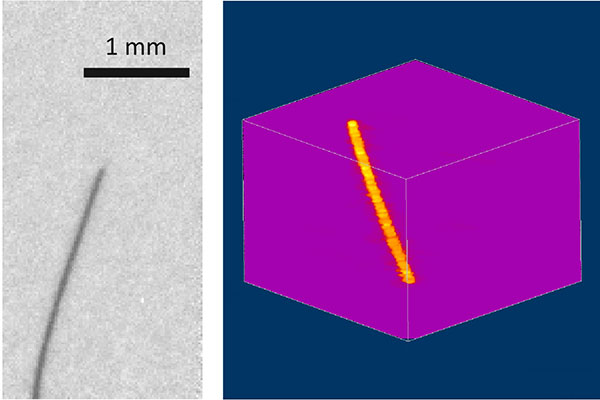 On the left is a projection image obtained with an exposure time of 1 ms whilst on the right is a three-dimensional reconstruction obtained from 32 projection images using a compressed-sensing algorithm. Image Credit: © Tohoku University.
On the left is a projection image obtained with an exposure time of 1 ms whilst on the right is a three-dimensional reconstruction obtained from 32 projection images using a compressed-sensing algorithm. Image Credit: © Tohoku University.
Under the guidance of Wataru Yashiro, a Professor at Tohoku University, a research group has designed a new technique that involves using intense synchrotron radiation that generates images of higher quality within a few milliseconds.
Currently, it is possible to perform high-resolution, high-speed X-ray CT using intense synchrotron radiation. But this needs samples to be rotated at high speed to capture images from several directions. This would render CT scans more similar to a rollercoaster ride!
Moreover, extreme rotation makes the control of the atmosphere or temperature of the sample challenging.
However, the researchers resolved this problem by developing an optical system that divides single synchrotron X-ray beams into several beams. These beams then shine onto the sample from several directions simultaneously. This avoids the need to rotate the sample.
Such a “multi-beam” technique is not simple since the direction of X-rays cannot be altered easily. In contrast to visible light, X-rays only have a weak interaction with matters, making it challenging to use prisms and mirrors to alter the route of the beams.
The researchers solved this issue by using micro-fabrication methods to make specifically shaped crystals. Then, such crystals were bent in the hyperbola shape. Joining three rows of crystals enabled the multi-beam optics to cover an angle of ±70°.
By performing their experiments at the SPring-8 synchrotron radiation facility, the researchers leveraged a highly advanced compressed-sensing algorithm that requires just a few dozen projection images for image reconstruction.
The invention makes 3-D observations of living beings and liquid samples within milliseconds possible. Its possible application is wide-spread, from fundamental material science to life sciences to industry.
Wataru Yashiro, Professor, Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
Journal Reference:
Voegeli, W., et al. (2020) Multibeam x-ray optical system for high-speed tomography. Optica. doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.384804.