May 26 2016
Two new optical devices could reduce the need to take tissue samples during medical examinations and operations and to then send them for testing - potentially speeding up diagnosis and treatment and cutting healthcare costs.
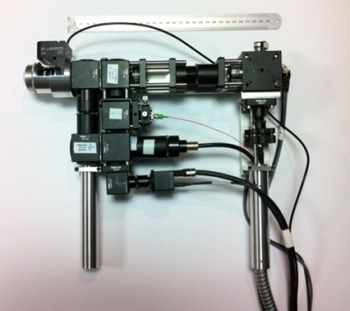 Lightweight handheld microscope. Credit: Imperial College London
Lightweight handheld microscope. Credit: Imperial College London
One is a lightweight handheld microscope designed to examine external tissue or tissue exposed during surgery. One example of its use could be to help surgeons compare normal and cancerous cells (during an operation). A key advantage is that the device can acquire high quality 3D images of parts of the body while patients are moving (eg due to normal breathing), enabling it to be applied to almost any exposed area of a patient's body.
The second instrument, a tiny endoscope* incorporating specially designed optical fibres and ultraprecise control of the light coupled into it, has the potential to be inserted into the body to carry out internal cell-scale examination, for example during neurosurgery. Ultimately, this new approach may be able to provide high resolution images enabling surgeons to see inside individual cells at an adjustable depth beneath the surface of the tissue.
Both prototypes have been developed by Imperial College London in collaboration with the University of Bath and funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
Currently, the diagnosis of many diseases requires taking a tissue specimen from the patient, preparing it in a laboratory, studying it under a microscope and then forwarding the results back to the clinician. The new devices, both of which harness a technique known as multiphoton excited fluorescence microscopy** to analyse individual cells in their native tissue, could be used in a consulting room or an operating theatre to help clinicians identify diseased tissue and provide a rapid diagnosis.
The handheld microscope incorporates a tracking mechanism that compensates for the patient's movements, ensuring the generation of steady images. The endoscope is just a fraction of a millimetre in diameter and has no moving parts. Both these devices use novel multicore optical fibres developed by Imperial's collaborators by the University of Bath.
Dr Chris Dunsby of Imperial College London, who has led the overall project, says: “These new devices open up exciting possibilities in the field of in-situ diagnosis and could help improve patient care in the future.”
Professor Jonathan Knight, who led the University of Bath team, says: “This has been a very exciting project which has enabled us to develop fibres with performance which we would have previously thought impossible.”
After further development and refinement of the technology, clinical trials will explore the healthcare benefits of the two devices in more detail, with the goal of beginning to introduce them into clinical use within around 5-10 years.
Notes for Editors
The 2.5 year research project Development of Multiphoton Microscopes for Real-World Clinical Applications ran from May 2013 to October 2015 and received total EPSRC funding of just over £854,000.
* An endoscope is a device that has a light attached to it and is used to look inside an organ or cavity within the body.
** This technique involves illuminating tissue with light of a specific wavelength that causes molecules in the tissue to emit light in response. This emission is called autofluorescence and can be used to form high-resolution images that could help determine whether, and to what extent, the tissue is diseased. Multiphoton excitation is where the required excitation is provided by two photons of half the required energy that are absorbed simultaneously. For tissue autofluorescence, this means that the illuminating photons can be near infrared rather than visible light and therefore can penetrate deeper into biological tissue - enabling 3D images to be produced up to ~0.1mm beneath the tissue surface in clinical instruments.
A photon is an elementary particle that comprises the smallest amount of light that can exist.
The Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)
As the main funding agency for engineering and physical sciences research, our vision is for the UK to be the best place in the world to Research, Discover and Innovate.
By investing £800 million a year in research and postgraduate training, we are building the knowledge and skills base needed to address the scientific and technological challenges facing the nation. Our portfolio covers a vast range of fields from healthcare technologies to structural engineering, manufacturing to mathematics, advanced materials to chemistry. The research we fund has impact across all sectors. It provides a platform for future economic development in the UK and improvements for everyone's health, lifestyle and culture.
We work collectively with our partners and other Research Councils on issues of common concern via Research Councils UK.
Imperial College London
Imperial College London is one of the world's leading universities. The College's 16,000 students and 8,000 staff are expanding the frontiers of knowledge in science, medicine, engineering and business, and translating their discoveries into benefits for society.
Founded in 1907, Imperial builds on a distinguished past - having pioneered penicillin, holography and fibre optics - to shape the future. Imperial researchers work across disciplines to improve health and wellbeing, understand the natural world, engineer novel solutions and lead the data revolution. This blend of academic excellence and its real-world application feeds into Imperial's exceptional learning environment, where students participate in research to push the limits of their degrees.
Imperial collaborates widely to achieve greater impact. It works with the NHS to improve healthcare in west London, is a leading partner in research and education within the European Union, and is the UK's number one research collaborator with China.
Imperial has nine London campuses, including its White City Campus: a research and innovation centre that is in its initial stages of development in west London. At White City, researchers, businesses and higher education partners will co-locate to create value from ideas on a global scale.
University of Bath
The University of Bath received its Royal Charter in 1966 and is now firmly established as a top ten UK university with a reputation for research and teaching excellence. Its campus, overlooking the UNESCO World Heritage City of Bath, has a vibrant research culture driven by the enthusiasm and invention of its academic community. The University is a sector leader in the commercial exploitation of intellectual property (IP) and the establishment of international links for exploitation of IP.