The advent of 3D machine vision technology and 3D cameras has opened up a wide range of new application areas which had previously been inaccessible to traditional 2D camera imaging or scanning tools.
Essentially, serving as the eyes of machinery, 3D machine vision cameras provide a 3D representation of space, allowing automated decision making based on, for example, the size and location of an object, its orientation or even its color.
3D machine vision technology has, therefore, become central to the design of many automated industrial processes, such as quality control, bin picking or in product assembly lines.
A recent interview with Dr. Martin Henneman from IDS Imaging Development Systems explored some of the potential uses of 3D machine vision in the industrial and transportation sectors, highlighting the benefits, features and key developments in the innovative Ensenso 3D camera series.
What has been the impact of 3D machine vision on automation technology and industrial processes?
3D machine vision has now established itself as a mainstream automation technology, used worldwide in conjunction with robotics for tasks like automated bin picking, pick and place, assembly operations or in logistics for depalletizing as part of intralogistics applications, such as those that handle and store goods or deliveries.
One of 3D machine vision technology’s biggest advantages is its ability to further reduce the need for human interaction in industrial processes. For example, an industrial setup will typically involve robots that automate difficult tasks or heavy lifting which becomes more flexible using 3D vision. Furthermore, robots that have been specifically developed to work in collaboration with or otherwise assist human employees emerge.
This is a growing, rapidly advancing area of research. One major drive is to provide robots with enough ‘visual sense‘ to allow them to exhibit smart behaviors and react adaptively to their environments.
Where do the Ensenso 3D cameras fit into the current machine vision field, and what benefits do they bring?
The Ensenso range of 3D cameras includes different active stereo vision 3D cameras and - recently added - the Ensenso S series which uses a 3D technology based on structured light. They are versatile enough to accommodate many applications, seeing regular use in both industrial and research applications worldwide.
Could you elaborate on the new Ensenso S model and some of its specific technological features?
The Ensenso S is a new member of the Ensenso portfolio and represents a new entry point to accurate 3D imaging at a lower price point than its relatives.
Despite its lower price, the Ensenso S features industry-grade design and interface options and a new 3D sensing technology using laser pattern triangulation, i.e., a variant of structured light, designed to facilitate innovative solutions for industrial applications.
The Ensenso S features an invisible infrared laser that creates a laser dot pattern. This is projected onto the scene.
For example, a pallet with a stack of boxes on top of it. The camera inside the Ensenso S images that scene, capturing the positions of these laser dots by recording where on the boxes the light from the laser dots is scattered back into the system.
This information is processed using the Ensenso software intelligence – an artificial neural network identifies the laser points individually, assigns each laser point an ID and then uses the principle of triangulation to acquire distance values for each of the laser points.
The camera itself is provided in a compact, robust package that features industrial housing, the camera, the laser and its diffraction element. The camera housing is built to IP65/67 specifications, meaning it can be safely used also in harsh environments.
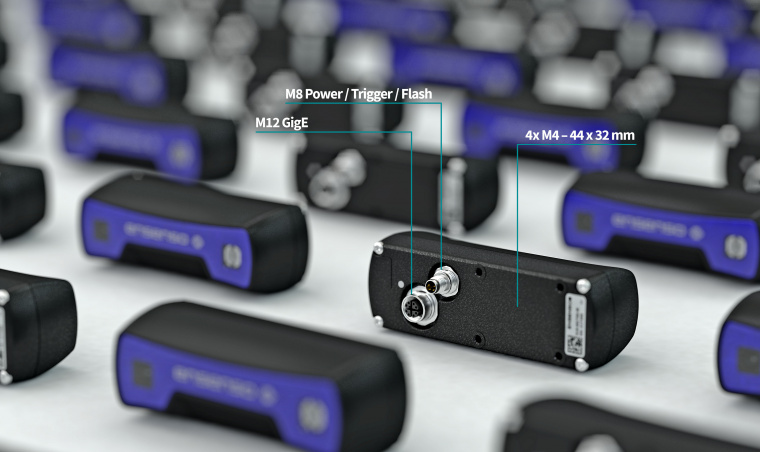
The back of the device features industrial connectors, including an M12 GigE data port for data transmission and an M8 port for power, trigger or flash connectivity. A full range of features is available on our website.
What sort of data can be acquired via the Ensenso S, and how can this be processed into applicable forms by operators and analysts?
The Ensenso S is able to provide high quality and comprehensive 3D point clouds. The camera’s laser pattern triangulation works with almost 90,000 laser points, has a view field of 60° horizontal x 50° vertical, and 500 to 3,000 mm working distance. The laser illumination enables varying exposure times, making even moving objects measurable. In terms of speed, 20 point clouds per second can be achieved with consistently high resolution at full projector power.
KI Laserpunkt Triangulation
The camera can provide high quality, low noise data able to detect details up to around a centimeter in size. It also offers a low artifact level when compared with a range of other technologies, such as low-cost stereo cameras and Time of Flight cameras.
Via the flexible programming interfaces, calibrated point clouds and comprehensive intermediate data are made available to the user’s choice of processing software for application integration.
Could you give our readers an overview of some example use cases of the Ensenso S 3D camera?
There are many ideal usage scenarios for the Ensenso S. In terms of logistics automation examples, the Ensenso S is ideal for handling pallets and monitoring the movement of goods around and in between busy areas like storage units.
When used in transport and movement applications, the Ensenso S can potentially detect obstacles that are in the way of transport vehicles. It is also an ideal choice for package handling. For example, an Ensenso S can be set up over a conveyor belt moving packages, and provide the 3D data for tracking and analyzing the packages.
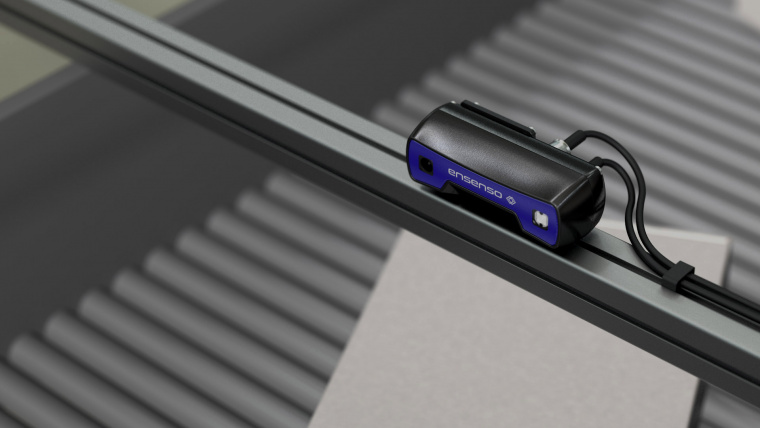

As already mentioned, the Ensenso S is ideal for use in combination with robots in depalletizing applications or even object recognition tasks requiring particular objects to be checked, recognized and controlled.
The Ensenso S is also opening up new application areas, for example, in horticulture where robots can tend to plants, monitor crops, survey fruits and pick them automatically and at the ideal time.
There is also a rapidly developing field of automated assistance, where robots collaborate with humans or even replace them for specific tasks, for example, selecting and transporting specific groceries from the store automatically and on demand.
In such complex and challenging scenarios the Ensenso S can enable that the situations ‘make sense’ to these intelligent systems.
What are the key takeaways that you would like our readers to remember about the Ensenso S 3D camera?
The Ensenso S represents a new entry point into accurate 3D imaging for a wide range of potential applications. This new, compact 3D camera is highly versatile, affordable and offers the potential to incorporate 3D vision also into applications that have not used this before based on required budget.
The innovative AI-powered pod and laser triangulation algorithm produces point clouds with accurate 3D geometry and a low artefact level, in particular when compared with the achievable results from other 3D technologies.
For integration the Ensenso S offers industry-grade housing and robust, comprehensive SDK features - all of which help make this new camera one of the most advanced and widely applicable devices available.
About Dr. Martin Hennemann
Dr. Martin Hennemann started at IDS in 2013 in System Consulting for 3D cameras and image processing. With his background in research and his expertise in image processing technologies and 3D sensing, he supports the further development of the IDS 3D product portfolio. Since 2018 he is product manager for 3D cameras and machine vision software.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH.
For more information on this source, please visit IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the interviewee and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited (T/A) AZoNetwork, the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and Conditions of use of this website.