Refraction is a phenomenon that occurs when waves passing from one transparent medium to another bend at the boundary between the two mediums due to a change in the speed of the waves.
A naturally occurring example of refraction is the rainbow, which is created when sunlight is refracted by raindrops. White light consists of different wavelengths, with blue having a shorter wavelength than red. When light passes through raindrops, the shorter wavelengths are bent more than the longer ones, splitting the light into its different colours.
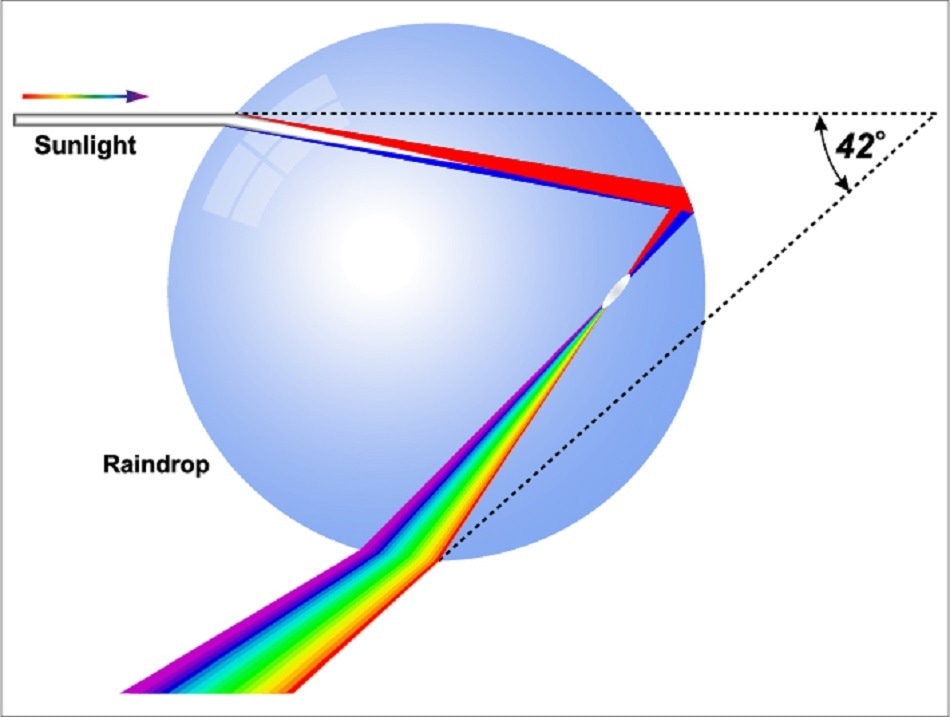
Image Credits: Fouad A. Saad/shutterstock.com
In optics, refraction occurs when waves pass from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with a differing refractive index at an oblique angle. The refraction phenomenon is mostly associated with light but can also be applied to other waves such as sound or water.
The refractive index, n, of a transparent medium is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the given medium. The formula is given by:
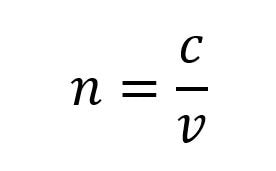
Where c is the speed of light in a vacuum and v is the speed of light in the desired medium
The amount of bending is based on the indices of refraction of the two media and is described quantitatively by Snell's Law. This relates the incident angle i and the refracted angle r (measured from the normal line N) to the refraction indices of the two media n1and n2.
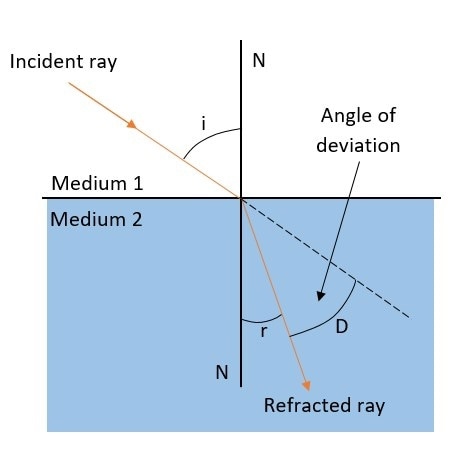
Snell’s law uses simple trigonometry to show that:
n1 sin i = n2 sin r
A vacuum has a refractive index of one, and air has a quoted refractive index of about 1.00029; however, this varies according to temperature and pressure. Generally, as the density of a material increases, so does its refractive index. Diamond has a very high refractive index of 2.417, and hence produces the sparkling effect.
Applications
The most common application of refraction is in the field of optics.
A lens is a transparent material that refracts light rays to converge at a single point. Lenses are designed in such a manner that light entering them is focused by refraction into a focal point, producing a magnified image of an object.
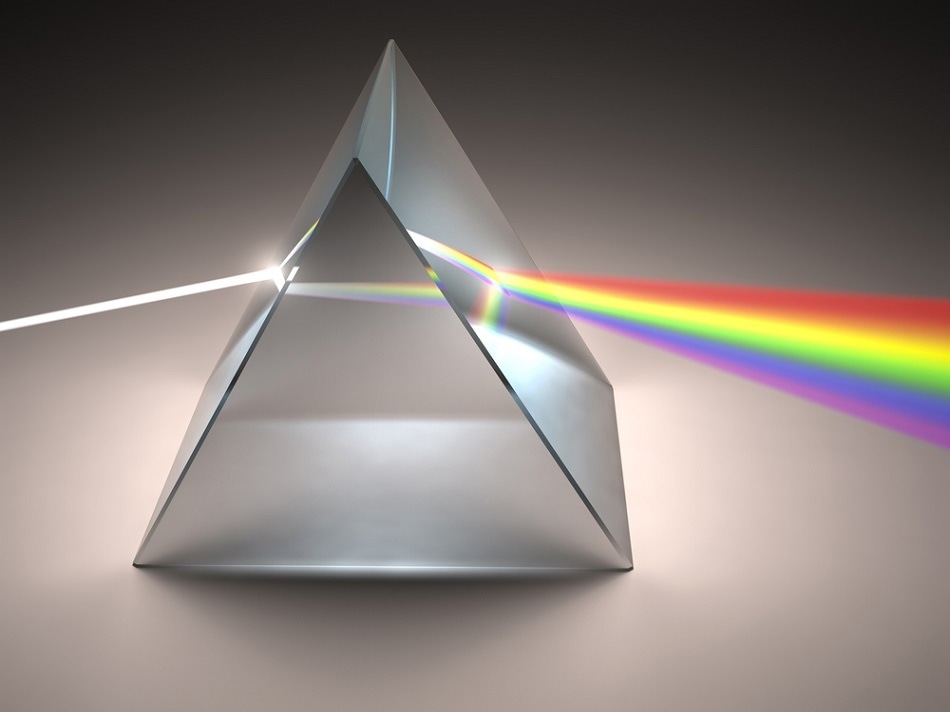
Image Credits: ktsdesign/shutterstock.com
Lenses are commonly used in binoculars and telescopes allowing for comprehensive images of distant objects, or in magnifying glasses and microscopes to view small objects, such as microorganisms, which are not visible to the naked eye. The human eye contains a convex lens that refracts light onto the retina for sight and can change shape to modulate the distance of focus.
Refraction is also used in prisms. A prism is a wedge-shaped device which causes incident light to be split into different colours. The refractive index of a material varies with the wavelength incident upon it, which results in a phenomenon called dispersion where the different wavelengths of light refract by different amounts and create a rainbow effect. This allows the light source to be studied in detail.
Sources and Further Reading
This article was updated on 1st August, 2018.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.