The launch of the Perseverance Mars rover will signify the 10th time that a Moxtek component has been launched into space flight. This rover, developed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), includes seven important instruments intended to explore and seek evidence of past life on Mars.
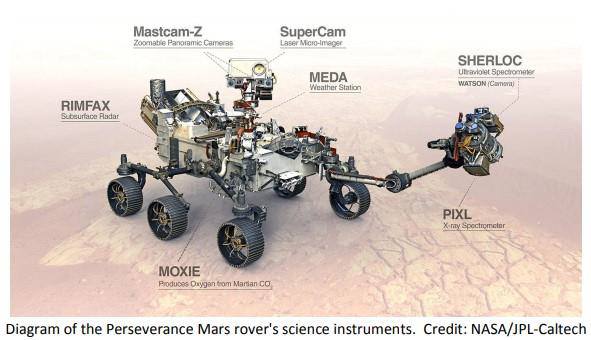
One of these instruments, the Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry (PIXL), is a compact x-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometer mounted at the end of the rover’s robotic arm and is designed to provide accurate identification of the elemental composition of rock and soil on Mar’s surface. The PIXL system uses three Moxtek components including a miniature x-ray tube and two DuraBeryllium x-ray detector windows.
NASA/JPL chose Moxtek x-ray windows because of their exceptional dependability in harsh and remote environments and chose the Moxtek x-ray tube because of its compact design, rigidity, and low-power consumption. The Moxtek x-ray tube was specifically designed to couple directly to an x-ray polycapillary optic, developed by X-ray Optical Systems (XOS), for the purpose of elemental mapping.
Moxtek’s x-ray tube and window enable the PIXL system to provide increased spatial resolution and improved measurement sensitivity. The PIXL system will analyse samples at each test site to determine the abundance and distribution of various chemical elements.
In 1996, Moxtek provided their first space flight component (x-ray window) to NASA/JPL onboard the Mars Sojourner rover. Since then NASA/JPL has used a Moxtek window on every Mars mission (Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, and now the Perseverance).